
An allergy is the body’s reaction to a substance that is normally harmless. With allergies, your child’s body sees the substance as harmful or foreign, and the immune system reacts to the substances, also known as allergens. Allergic reactions are common; in fact, they affect up to 40% of children in the United States.
Read more below about allergies in children, their causes, common symptoms, and severe reactions. Understand how allergies are diagnosed through tests and exams.

The immune system is the body’s natural defense against bacteria, viruses, and other foreign substances.
Before your child can have a reaction to a particular substance, the immune system must first be sensitive to it. Usually this means your child’s body must be exposed to the substance at least once. Once it is sensitive to it, your child’s body will react every time your child has contact with the substance. Most reactions are mild, but some are life-threatening.
Unfortunately, many things can cause an allergic reaction. Your child’s body may react to an allergen when breathing, swallowing, or touching it. Luckily, children often outgrow food allergies when they become adults.
It’s worth noting that your child may have an increased risk of a reaction if other people in your family have allergies too.
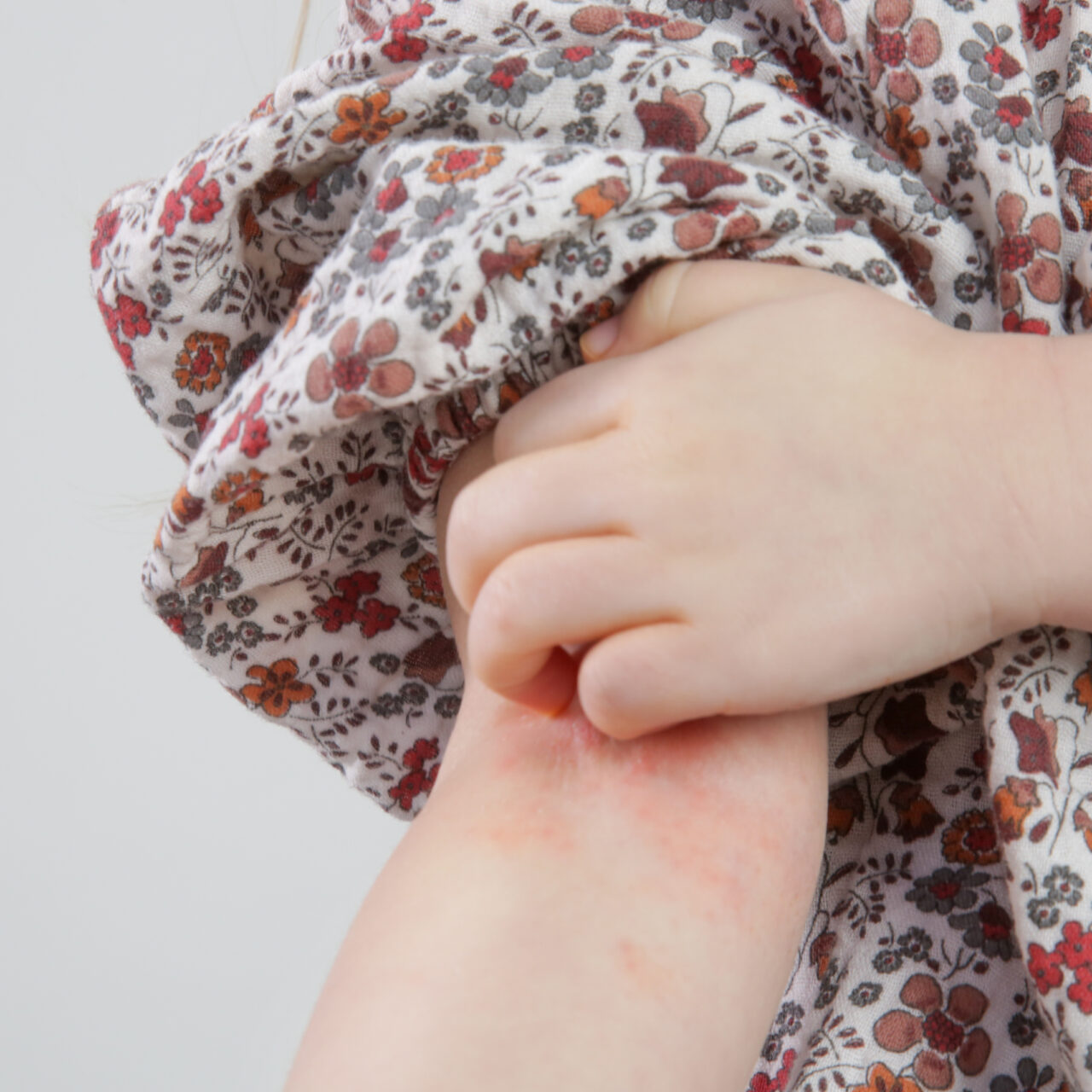

Allergy symptoms may go away in a few minutes without treatment, or they may last for several days.
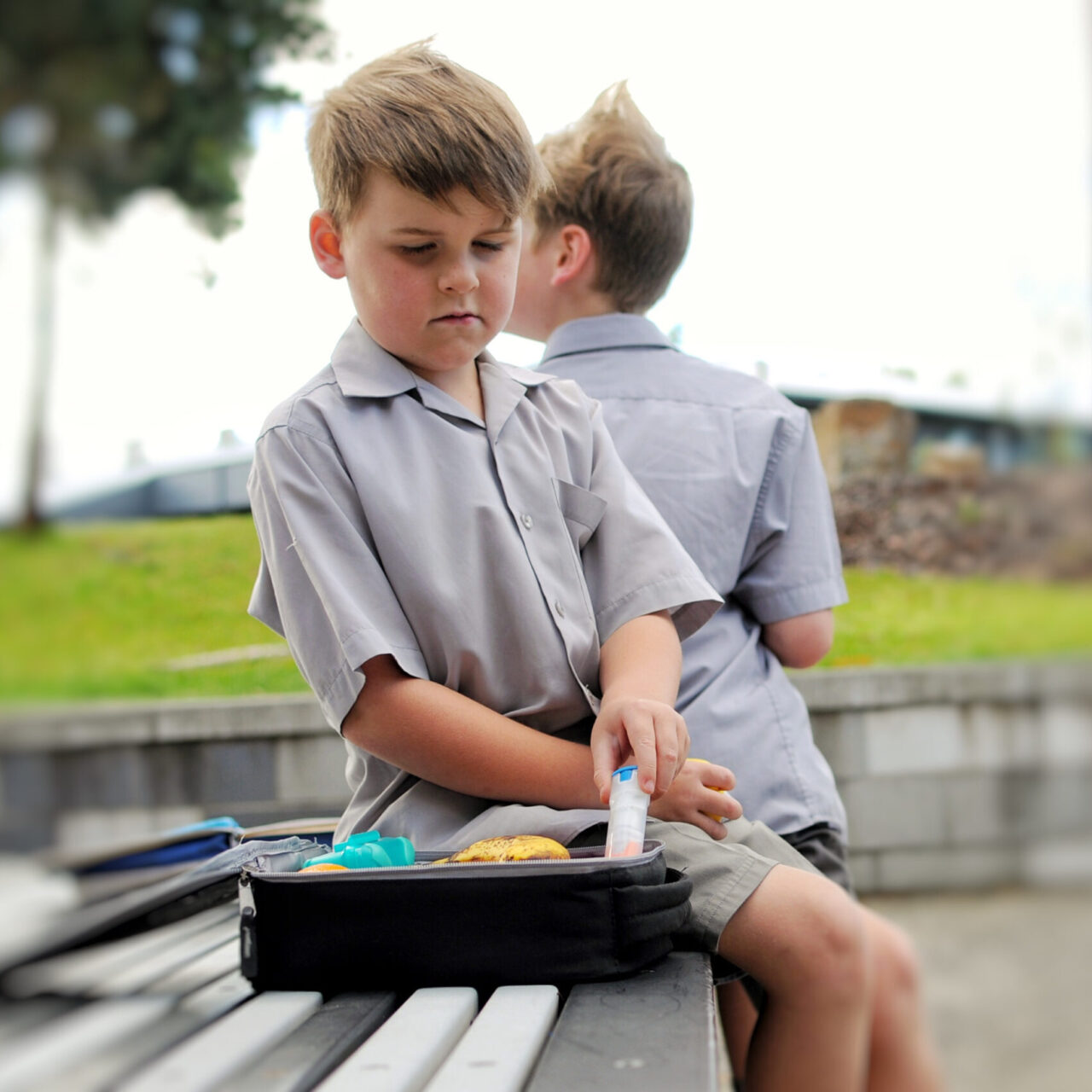

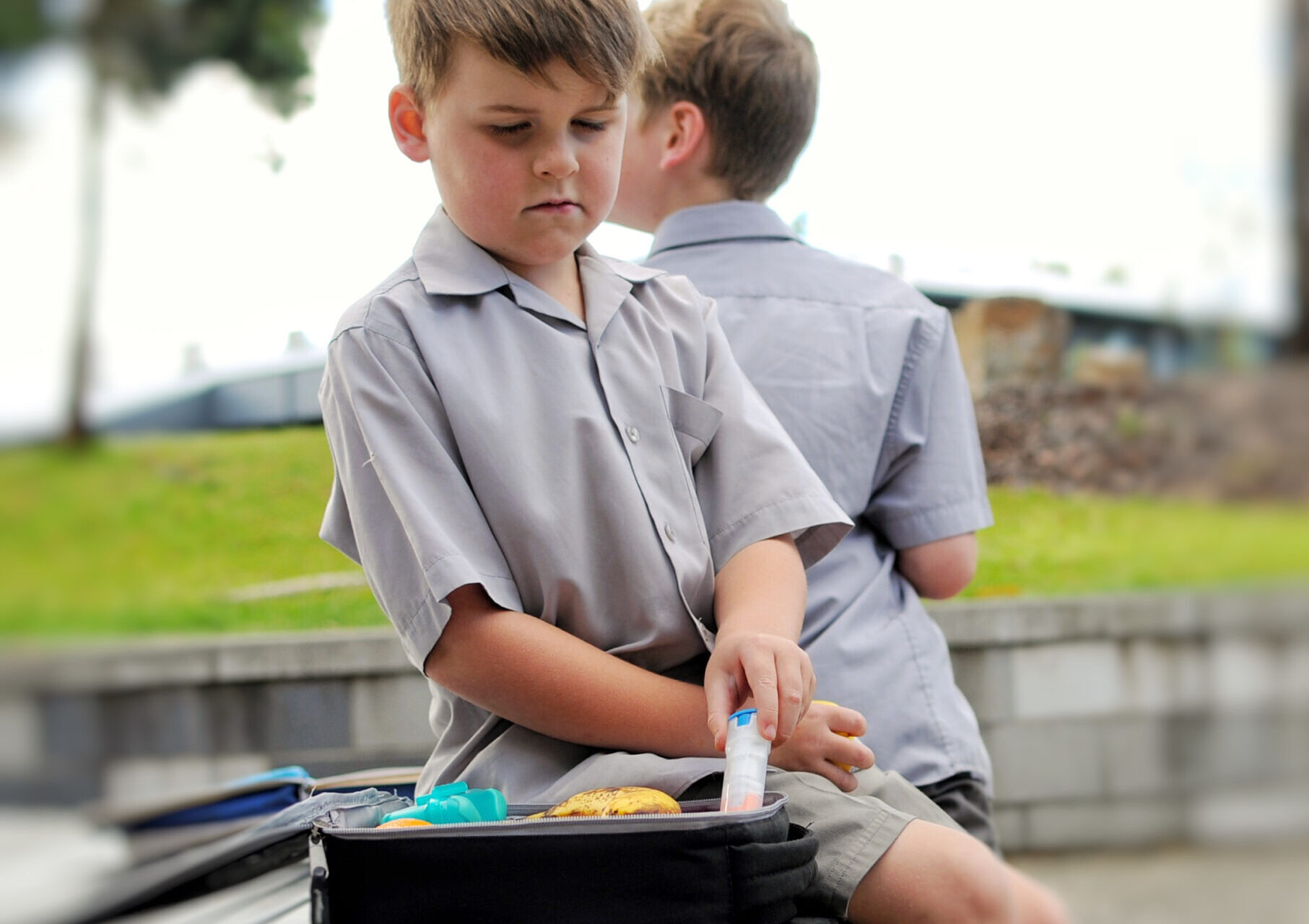
Sometimes an allergic reaction may be severe. This is called anaphylaxis and it is a life-threatening emergency – call 911 immediately if this occurs because it can affect the whole body within minutes. Insect stings, certain foods, and drugs such as penicillin are some of the more common causes of severe allergic reactions.
Your child’s healthcare provider will ask about his or her symptoms, review medical history, and examine your little one thoroughly. Most common allergies can be diagnosed from your child’s history and a physical exam.
Showing 13–14 of 14 Results